Understanding Capacitors: The Powerhouse of Electronic Circuits

Capacitors are everywhere—from the tiny circuits in your smartphone to the massive power systems that keep cities running. But what makes capacitors so essential? In this blog post, we’ll explore what a capacitor is, how it works, and why it’s a fundamental component in electronics.
What is a Capacitor?
A capacitor is an electrical component that stores and releases electrical energy. Think of it as a small battery that charges and discharges rapidly. While it doesn’t store energy in the same way a battery does, a capacitor can quickly release the stored energy when needed, making it incredibly useful in a wide variety of applications.

How Does a Capacitor Work?
A capacitor consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material called a dielectric. When voltage is applied across the plates, an electric field develops, causing positive charges to accumulate on one plate and negative charges on the other. This separation of charges creates an electric potential, or voltage, across the capacitor, allowing it to store energy.
The amount of charge a capacitor can store depends on two factors:
- Capacitance: Measured in farads (F), capacitance is determined by the surface area of the plates, the distance between them, and the type of dielectric material used.
- Voltage: The maximum voltage a capacitor can handle before the dielectric material breaks down, leading to a failure of the capacitor.
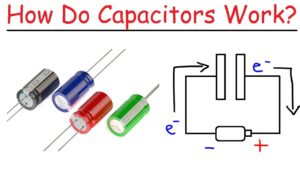
Why Are Capacitors Important?
Capacitors serve many vital roles in electronic circuits:
Energy Storage: Capacitors can store and release energy quickly, making them useful for applications where rapid bursts of energy are needed, such as in camera flashes or defibrillators.
Filtering: In power supplies, capacitors are used to filter out noise and smooth fluctuations in voltage, ensuring stable operation of electronic devices.
Timing Circuits: Capacitors are often used with resistors to create timing circuits, like those in blinkers, oscillators, and clocks. The time it takes for a capacitor to charge or discharge determines the timing of these circuits.
Signal Coupling and Decoupling: Capacitors can block DC signals while allowing AC signals to pass, which is essential in audio and radio frequency circuits for separating different stages of signal processing.
Types of Capacitors
There are various types of capacitors, each suited to different applications:
Ceramic Capacitors: These are small, inexpensive capacitors made from ceramic materials. They’re used for high-frequency applications and general-purpose use.
Electrolytic Capacitors: These capacitors have high capacitance values and are often used in power supply circuits for filtering and energy storage. They have a polarity, meaning they must be connected correctly to function.
Tantalum Capacitors: These capacitors are known for their small size and high capacitance. They are often used in mobile devices and computers where space is limited.
Film Capacitors: Made from plastic films, these capacitors are highly stable and reliable, ideal for precision circuits like audio equipment.
Supercapacitors: Also known as ultracapacitors, these are designed for energy storage applications that require very high capacitance. They can store more energy than traditional capacitors and are used in backup power systems, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems.

Practical Example: Using Capacitors in a Circuit
Let’s look at a simple example: a power supply circuit. When converting AC (alternating current) from the wall outlet to DC (direct current) needed by most electronic devices, capacitors are used to smooth out the ripples in the DC voltage, ensuring a stable supply. Without capacitors, devices like your laptop or smartphone would be much less efficient and prone to malfunction.
So next time you open up a gadget or work on an electronics project, take a moment to appreciate these tiny but mighty components that keep the electronic world running smoothly!
#LearnRobotics #XRobotics #AI #STEM #TechEducation #Capacitor #RoboticsDevelopment #Innovation
